

Nodes are regions where the probability of finding an electron is ZERO.Ī sigma-bond is an "end-to-end" bond formed from symmetric atomic orbitals. It is important to notice that the phase signs do NOT symbolize charges. A node occurs if the phase signs change from (+) to (-) or vice versa. Phases are designated either (+) or (-) relative to their wave "up" or wave "down" displacements. Note how the bonding orbitals come together constructively, while the antibonding orbitals do not. "Bonding" orbitals are less energetic than antibonding atomic orbitals and are in-phase, as depicted in the figure below. Orbitals that are out-of-phase with one of another are "antibonding" orbitals because regions with dense electron probabilities do not merge which destabilizes the molecule. Molecules consisting of two non-identical atoms are said to be heteronuclear diatomic, such as: CO, NO, HF, and LiF. Molecules consisting of two identical atoms are said to be homonuclear diatomic, such as: H 2, N 2, O 2, and F 2. A MO is defined as the combination of atomic orbitals. The region an electron is most likely to be found in a molecule. These steps may then be extrapolated to construct more difficult polyatomic diagrams. The objective of this wiki is to provide readers with the fundamental steps in constructing simple homonuclear and heteronuclear diatomic molecular orbital diagrams.
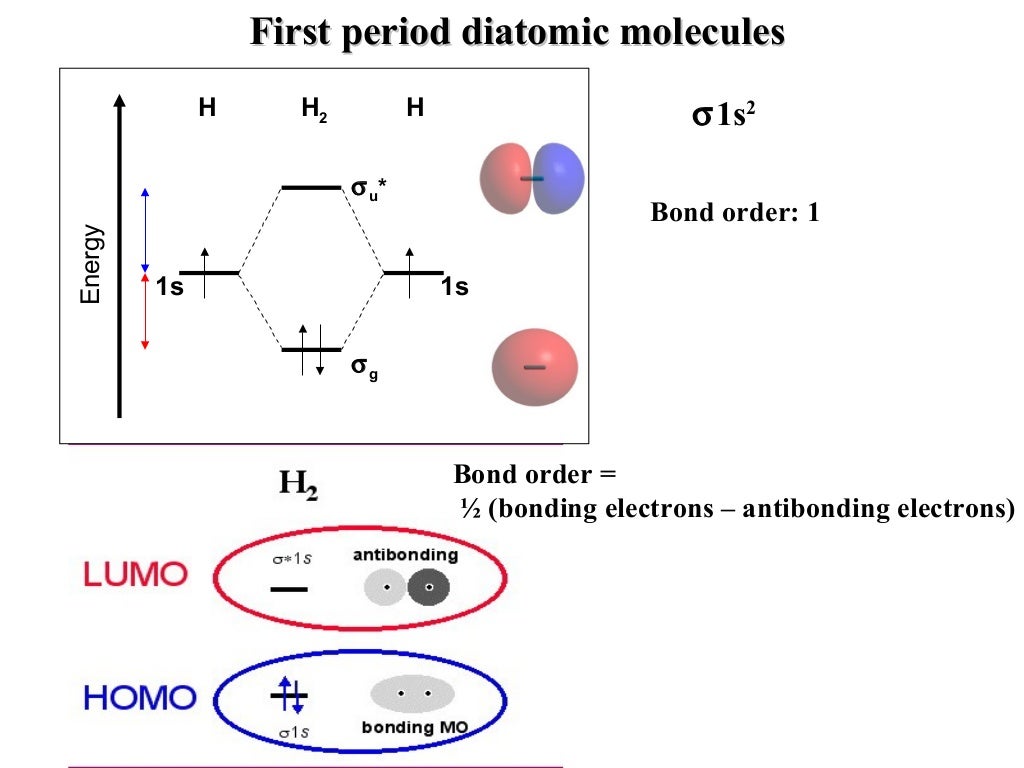
They also provide information in predicting a molecule’s electronic spectra and paramagnetism. MO diagrams predict physical and chemical properties of a molecule such as shape, bond energy, bond length and bond angle.
The MO theory incorporates the wave character of electrons in developing MO diagrams. \)Īlthough VSEPR and the Valence Bond theory accurately predict bond properties, they fail to fully explain some molecules.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
